Autism was formerly called a disease, but now it is rather described as a developmental disorder or another pattern of brain function.
Symptoms of autism are different from commonly accepted ways of communicating, establishing relationships, and expressing emotions. Autistic people also learn and get to know the world differently than their peers.
The causes of autism are not fully understood, but there is no doubt that genetic predisposition is of great importance. At the same time, the presence of autism-specific gene mutations in the genotype does not mean that autistic traits will definitely develop. It is likely that environmental factors such as metabolic problems, perinatal damage to the nervous system, or parents' high age also contribute to autistic behavioral patterns.
Diagnosis and treatment of autism
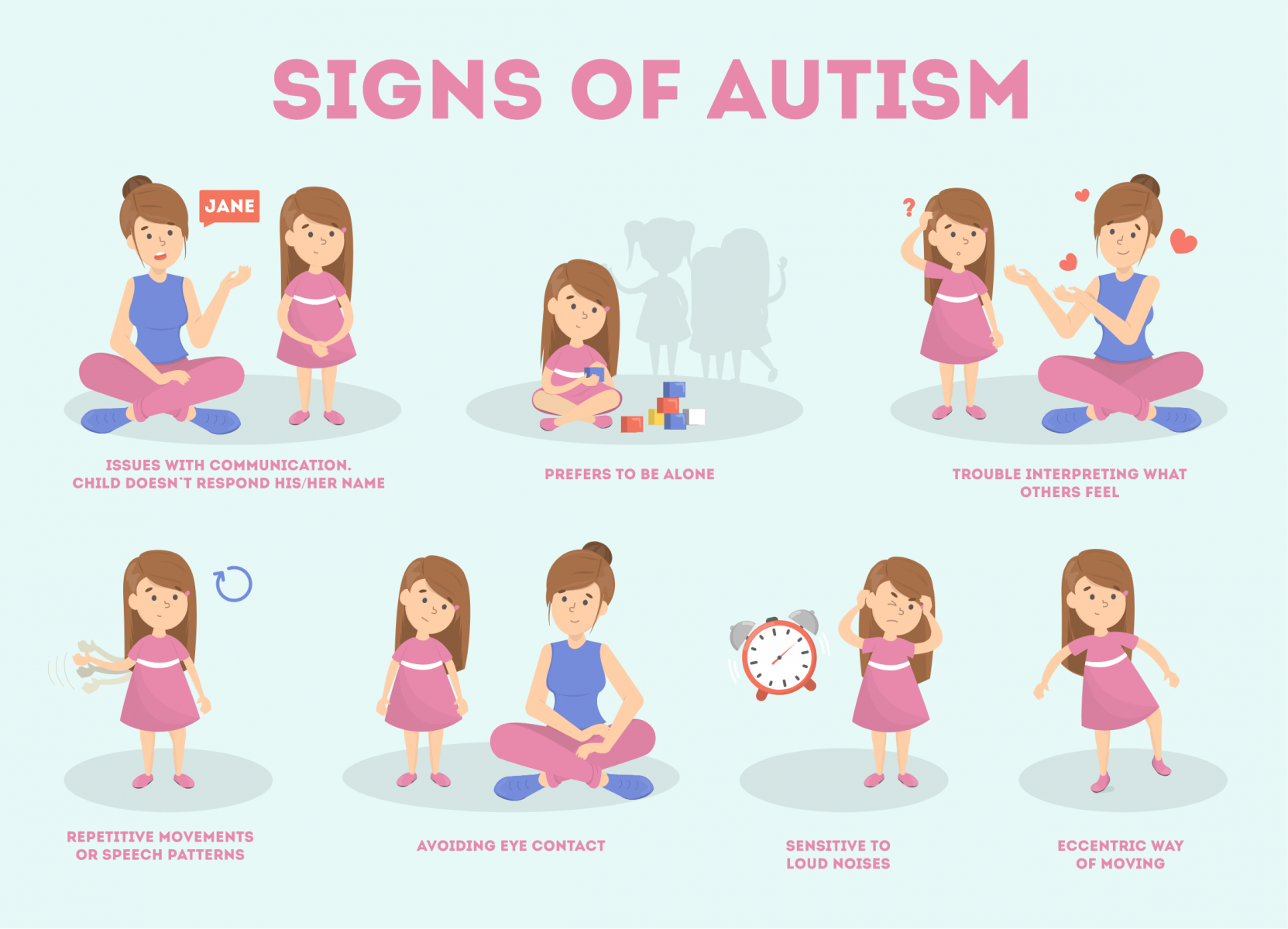
According to the classification of disorders and diseases DMS-V and ICD 10, typical for autism are, among others features such as:
delay or lack of speech development, non-standard use of expressions, strong attachment to routine activities and rituals, lack of reaction to other people's emotions or unusual reactions and not showing the need for social contacts.
These behaviors are visible from an early age, however, autism in children is not always correctly diagnosed, because autistic traits are of varying intensity. That is why the term autism spectrum is often used .
Autism is not a disease, so its treatment is not possible. Autistic people, however, can be supported and facilitated their functioning in society.
Help includes equipping people with autism with skills enabling communication with the environment. Currently, the so-called developmental approach, taking into account the unique characteristics of the person taking part in the therapy.
